When it comes to understanding when it gets dark, various factors come into play, including geographical location, time of year, and local weather conditions. This article will delve into the science of daylight, the concept of dusk and twilight, and how these factors influence when darkness falls. We will also cover the implications of darkness on human activities, health, and safety.
Understanding Daylight and Darkness
Daylight refers to the natural light provided by the sun during the day, while darkness is the absence of light. The transition from daylight to darkness occurs at sunset, which varies depending on the time of year and geographical location.
The Science of Daylight
The Earth rotates on its axis, causing different parts of the planet to experience sunlight at different times. This rotation, combined with the tilt of the Earth’s axis, results in the changing length of days and nights throughout the year.
- Equinoxes and Solstices: The equinoxes occur around March 21 and September 23, when day and night are approximately equal in length. The solstices occur around June 21 and December 21, marking the longest and shortest days of the year, respectively.
- Latitude: The latitude of a location significantly affects the amount of daylight it receives. Areas closer to the equator experience relatively consistent daylight hours throughout the year, while regions closer to the poles experience extreme variations, with long days in summer and long nights in winter.
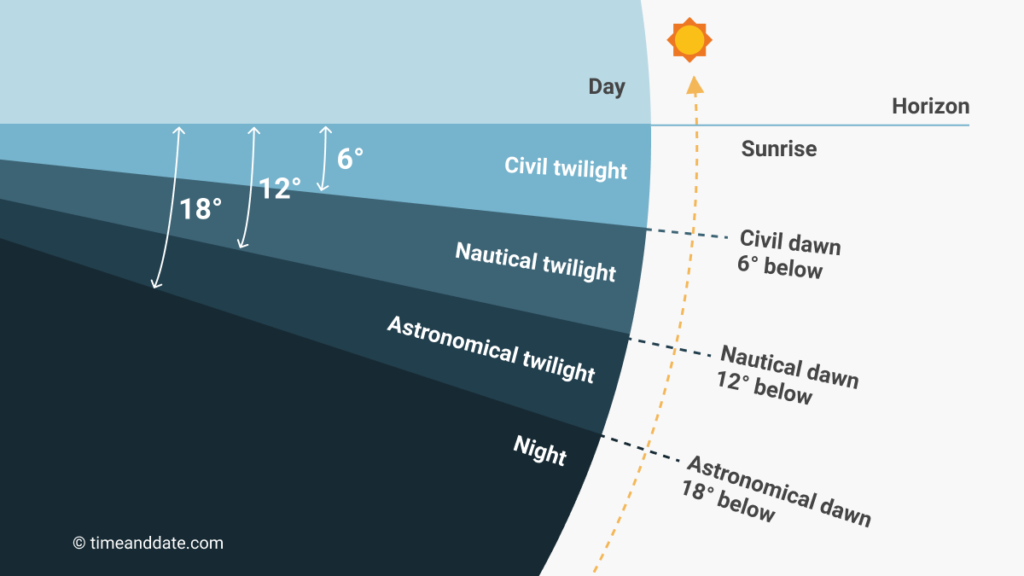
Dusk and Twilight
The transition from day to night involves several phases, including dusk and twilight.
- Dusk: Dusk is the period of time after sunset when the sky is partially illuminated. It can be divided into three phases:
- Civil Twilight: The first phase of dusk, when the sun is just below the horizon, and there is enough natural light for most outdoor activities. In this phase, artificial lighting may not be necessary.
- Nautical Twilight: The second phase, occurring when the sun is between 6 and 12 degrees below the horizon. During this time, the horizon is still visible at sea, allowing sailors to navigate using stars.
- Astronomical Twilight: The final phase, when the sun is between 12 and 18 degrees below the horizon. At this point, the sky is dark enough for astronomers to observe celestial objects without interference from sunlight.
- Night: Night begins after astronomical twilight, when the sky is fully dark. The duration of night varies based on geographical location and the time of year.
Factors Influencing When It Gets Dark
Several factors can influence the timing of darkness, including:
1. Geographical Location
The latitude and longitude of a location play a significant role in determining when it gets dark. For example, cities near the equator, such as Quito, Ecuador, experience relatively consistent sunset times throughout the year, typically around 6 PM. In contrast, cities further north or south, such as Reykjavik, Iceland, can experience significant variations in sunset times, ranging from around 3 PM in winter to nearly midnight in summer.
2. Time of Year
The time of year affects the length of daylight and the timing of sunset. During the summer months, days are longer, and sunset occurs later. Conversely, in winter, days are shorter, and sunset occurs earlier.
3. Local Weather Conditions
Weather conditions can also impact the perception of darkness. Overcast skies or heavy precipitation can make it feel darker earlier in the day, while clear skies may extend the perception of daylight.
Measuring Sunset and Darkness
Sunset times can be measured using various tools and methods:
1. Solar Calculators
Solar calculators are tools that can provide precise sunset and sunrise times based on geographical location and date. Many online resources and smartphone applications can calculate these times, taking into account factors such as latitude and longitude.
2. Almanacs
Almanacs, such as the Farmer’s Almanac, provide annual data on sunrise and sunset times for various locations. These publications often include charts and tables that outline the times throughout the year.
3. Observational Methods
Individuals can also observe changes in natural light to determine when it gets dark. Noticing the transition from bright daylight to the dimming of colors in the environment can help gauge the timing of dusk and darkness.
Implications of Darkness
The onset of darkness has various implications for human activities, health, and safety:
1. Impact on Daily Activities
The arrival of darkness can signal the end of outdoor activities and the beginning of nighttime routines. Many people adjust their schedules based on daylight availability, with increased activity during daylight hours and a shift to indoor activities after dark.
2. Health Considerations
Exposure to natural light during the day is essential for maintaining circadian rhythms, which regulate sleep-wake cycles. Insufficient exposure to daylight can lead to sleep disturbances, mood disorders, and other health issues. Conversely, darkness signals the body to produce melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep.
3. Safety Concerns
Darkness can pose safety risks, particularly for outdoor activities. Reduced visibility can increase the likelihood of accidents and injuries. It is essential to take precautions, such as using proper lighting and being aware of surroundings, when engaging in activities after dark.
Table: Sunset Times in Various Locations
| Location | Latitude | Average Sunset Time (Summer) | Average Sunset Time (Winter) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quito, Ecuador | 0.2295° S | 6:00 PM | 6:00 PM |
| Reykjavik, Iceland | 64.1355° N | 11:30 PM | 3:00 PM |
| New York City, USA | 40.7128° N | 8:30 PM | 4:00 PM |
| Sydney, Australia | 33.8688° S | 8:00 PM | 5:30 PM |
| London, UK | 51.5074° N | 9:00 PM | 4:00 PM |
Conclusion
Understanding when it gets dark involves considering various factors, including geographical location, time of year, and local weather conditions. The transition from daylight to darkness is marked by phases such as dusk and twilight, which influence human activities and health. By measuring sunset times and being aware of the implications of darkness, individuals can better navigate their daily routines and ensure safety during nighttime activities.
FAQ Section
When does it get dark?
The time it gets dark varies based on geographical location, time of year, and local weather conditions. Sunset times can range from early afternoon in winter to late evening in summer.
What is dusk?
Dusk is the period of time after sunset when the sky is partially illuminated. It can be divided into civil twilight, nautical twilight, and astronomical twilight.
How does latitude affect sunset times?
Locations closer to the equator experience relatively consistent sunset times throughout the year, while regions closer to the poles experience significant variations in sunset times.
What tools can I use to measure sunset times?
Solar calculators, almanacs, and observational methods can all be used to determine sunset times and the onset of darkness.
How does darkness impact health?
Insufficient exposure to natural light can disrupt circadian rhythms and lead to sleep disturbances and mood disorders. Darkness signals the body to produce melatonin, promoting sleep.
Where can I find more information about daylight and darkness?
For more detailed information, you can visit the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) website, which provides resources on daylight patterns and related topics.By understanding the factors that influence when it gets dark, individuals can better plan their activities and prioritize health and safety during the nighttime hours.