Understanding Non-Lateral Markers: What They Indicate
In the realm of navigation, particularly in maritime and boating contexts, markers serve as essential tools for ensuring safe passage and guiding vessels through various waterways. Among these markers, non-lateral markers play a significant role in conveying important information to boaters and navigators. This article will delve into the meaning of non-lateral markers, their types, purposes, and how to interpret them effectively.
What Are Non-Lateral Markers?
Non-lateral markers are navigational aids that provide information about specific areas, hazards, or regulations in a waterway, rather than indicating the sides of a channel like lateral markers do. Lateral markers, such as buoys, are used to mark the edges of navigable channels and guide vessels safely through them. In contrast, non-lateral markers convey information about dangers, controlled areas, and other important navigational details.
Types of Non-Lateral Markers
Non-lateral markers can be categorized into several types, each serving a distinct purpose. The following are the most common types of non-lateral markers:
- Regulatory Markers: These markers indicate specific rules or regulations that apply to a particular area. They may include speed limits, no-wake zones, or areas where fishing is prohibited. Regulatory markers are typically square or rectangular in shape and are colored orange and white.
- Information Markers: Information markers provide general information about the area, such as nearby facilities, services, or points of interest. They may indicate locations for food, supplies, or repairs and are usually square or rectangular with orange lettering on a white background.
- Danger Markers: Danger markers warn boaters of potential hazards in the water, such as rocks, shoals, or construction areas. These markers are typically diamond-shaped and are colored yellow with black symbols or text.
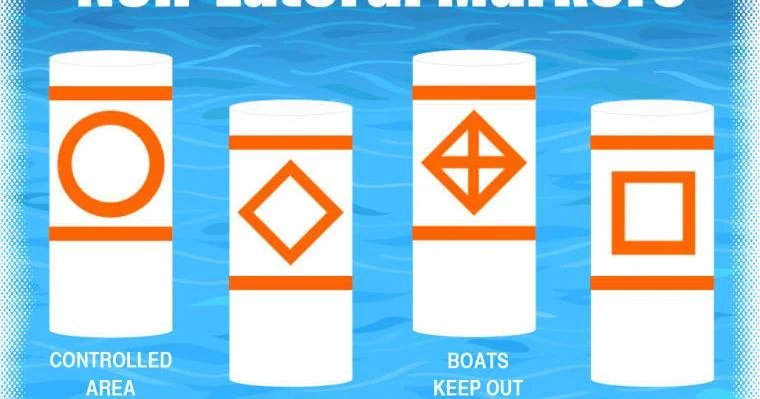
- Exclusion Markers: Exclusion markers indicate areas that are off-limits to all vessels, such as swimming areas, dams, or spillways. These markers are usually marked with a crossed diamond shape and are colored yellow and black.
- Controlled Area Markers: Controlled area markers indicate specific zones where particular rules apply, such as no-wake zones or idle speed areas. These markers are usually circular and colored with orange and white.
Summary Table of Non-Lateral Markers
| Marker Type | Shape | Color | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Marker | Square/Rectangular | Orange and White | Indicates rules or regulations |
| Information Marker | Square/Rectangular | Orange and White | Provides general information |
| Danger Marker | Diamond | Yellow with Black | Warns of hazards in the water |
| Exclusion Marker | Crossed Diamond | Yellow and Black | Indicates off-limits areas |
| Controlled Area Marker | Circle | Orange and White | Designates areas with specific rules |
Purpose of Non-Lateral Markers
Non-lateral markers serve several critical purposes in navigation:
- Safety: These markers help ensure the safety of boaters by providing warnings about potential hazards and indicating areas that should be avoided.
- Regulation Compliance: Regulatory markers inform boaters of the rules and regulations that apply to specific areas, helping to maintain order and prevent accidents.
- Navigation Assistance: Information markers help boaters locate essential services and facilities, enhancing their overall experience on the water.
- Environmental Protection: Exclusion markers protect sensitive areas, such as wildlife habitats or swimming zones, by keeping boats at a safe distance.
How to Interpret Non-Lateral Markers
Understanding how to interpret non-lateral markers is essential for safe navigation. Here are some tips for interpreting these markers effectively:
- Familiarize Yourself with Shapes and Colors: Knowing the shapes and colors associated with different types of markers is crucial. For example, yellow markers indicate hazards, while orange markers convey regulations.
- Read the Text: Many non-lateral markers include text that provides specific information. Always take a moment to read the text on the marker to understand the rules or warnings associated with that area.
- Use Charts and Maps: Nautical charts and maps often include information about non-lateral markers in the area. Familiarize yourself with these resources before heading out on the water.
- Stay Alert: Always remain vigilant while navigating, especially in unfamiliar waters. Keep an eye out for markers and be prepared to adjust your course as needed.
- Consult Local Regulations: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding non-lateral markers. Always consult local boating regulations to ensure compliance.
The Importance of Non-Lateral Markers in Navigation
Non-lateral markers play a vital role in maintaining safe navigation on waterways. They provide essential information that helps boaters make informed decisions and navigate safely. Here are some key reasons why non-lateral markers are important:
- Accident Prevention: By warning boaters of hazards and indicating off-limits areas, non-lateral markers help prevent accidents and injuries on the water.
- Environmental Conservation: Exclusion markers protect sensitive ecosystems and wildlife habitats, promoting environmental conservation and responsible boating practices.
- Enhanced Navigation: Information markers provide valuable insights into nearby facilities and services, making it easier for boaters to plan their trips and find necessary resources.
- Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory markers ensure that boaters are aware of and comply with local laws and regulations, contributing to a safer boating environment for everyone.
Conclusion
Non-lateral markers are essential navigational aids that provide crucial information for boaters. Understanding the different types of non-lateral markers, their purposes, and how to interpret them is vital for safe navigation on the water. By being aware of these markers and their significance, boaters can enhance their safety, comply with regulations, and enjoy their time on the water.
FAQ Section
Q1: What are non-lateral markers?
A1: Non-lateral markers are navigational aids that provide information about specific areas, hazards, or regulations in a waterway, rather than indicating the sides of a channel.
Q2: What are the different types of non-lateral markers?
A2: The different types of non-lateral markers include regulatory markers, information markers, danger markers, exclusion markers, and controlled area markers.
Q3: How do I interpret non-lateral markers?
A3: To interpret non-lateral markers, familiarize yourself with their shapes and colors, read any text on the marker, use nautical charts, stay alert while navigating, and consult local regulations.
Q4: Why are non-lateral markers important?
A4: Non-lateral markers are important for accident prevention, environmental conservation, enhanced navigation, and regulatory compliance.
Q5: Can non-lateral markers be found in all waterways?
A5: Non-lateral markers are commonly found in navigable waterways, including rivers, lakes, and coastal areas. However, their presence may vary depending on the region and local regulations.
Q6: What do regulatory markers indicate?
A6: Regulatory markers indicate specific rules or regulations that apply to a particular area, such as speed limits or no-wake zones.
Q7: What should I do if I see a danger marker?
A7: If you see a danger marker, proceed with caution and be aware of the hazards indicated. Adjust your course as necessary to avoid the danger.
Q8: Are there penalties for ignoring non-lateral markers?
A8: Yes, ignoring non-lateral markers can result in fines, penalties, or accidents. It is essential to adhere to the information provided by these markers for safe navigation.
Q9: How can I find more information about boating regulations and markers?
A9: For more detailed information, you can visit the U.S. Coast Guard website dedicated to boating safety and regulations.
Q10: Where can I learn more about non-lateral markers?
A10: For more detailed information, you can visit the Wikipedia page dedicated to nautical markers.
Summary Table
| Marker Type | Shape | Color | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Marker | Square/Rectangular | Orange and White | Indicates rules or regulations |
| Information Marker | Square/Rectangular | Orange and White | Provides general information |
| Danger Marker | Diamond | Yellow with Black | Warns of hazards in the water |
| Exclusion Marker | Crossed Diamond | Yellow and Black | Indicates off-limits areas |
| Controlled Area Marker | Circle | Orange and White | Designates areas with specific rules |
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth understanding of non-lateral markers, their types, purposes, and importance in navigation. By familiarizing yourself with these markers, you can enhance your safety and enjoyment while boating.