Understanding Safeguarding Devices: Protecting Workers in Industrial Environments
Introduction
In industrial settings, the safety of workers is paramount. With the increasing complexity and automation of machinery, safeguarding devices have become essential in protecting workers from potential hazards. These devices are designed to prevent accidents, injuries, and fatalities by mitigating risks associated with operating machinery. This article explores the various types of safeguarding devices, their functions, and their significance in promoting workplace safety.
What Are Safeguarding Devices?
Safeguarding devices are mechanisms or systems designed to protect workers from the hazards associated with machinery. They can take various forms, including physical barriers, electronic sensors, and control systems. The primary goal of these devices is to prevent access to dangerous areas, detect the presence of workers in hazardous zones, and ensure that machinery operates safely.
Types of Safeguarding Devices
There are several types of safeguarding devices, each serving a specific function to enhance worker safety. Below are some of the most common types:
1. Presence-Sensing Devices
Presence-sensing devices, such as light curtains and laser scanners, detect the presence of a person or object in a hazardous area. When an operator or an object enters the danger zone, these devices can automatically stop the machine’s operation, preventing potential injuries.
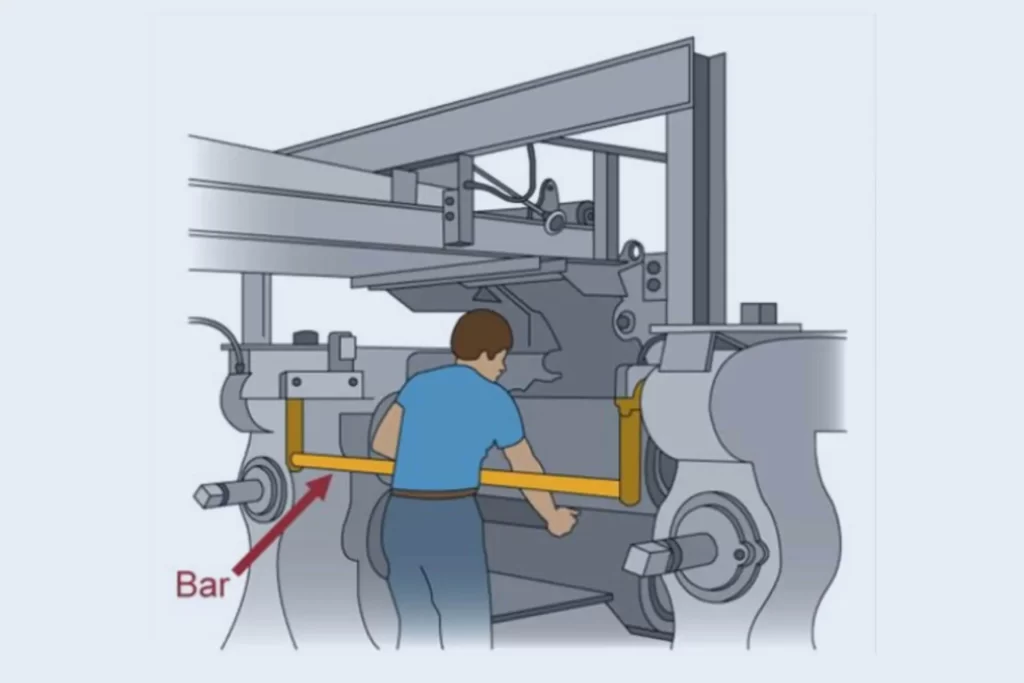
2. Pullback Devices
Pullback devices are designed to retract an operator’s hands or arms from the danger zone when the machine is in operation. These devices are typically attached to the operator’s hands and ensure that they are safely withdrawn before the machine can start.
3. Restraint Devices
Restraint devices, such as cables or straps, limit the movement of an operator’s hands, ensuring they cannot reach hazardous areas while the machine is in operation. This helps to keep body parts away from potential injury zones.
4. Safety Trip Controls
Safety trip controls allow operators to quickly stop machinery in case of an emergency. These controls can be activated by a pressure-sensitive bar or a foot pedal, providing a rapid response to potential hazards.
5. Two-Hand Control Devices
Two-hand control devices require the operator to use both hands to start the machine. This design ensures that the operator’s hands are kept away from the danger zone during operation, reducing the risk of accidental contact with moving parts.
6. Two-Hand Trip Devices
Similar to two-hand control devices, two-hand trip devices require the operator to press two buttons simultaneously to activate the machine. This feature ensures that the operator’s hands remain clear of the hazardous area while the machine is in operation.
Functions of Safeguarding Devices
Safeguarding devices perform several critical functions that contribute to workplace safety:
Prevent Access to Hazardous Areas
Many safeguarding devices create physical barriers or employ electronic sensors to prevent workers from entering dangerous zones. This is crucial in protecting workers from moving parts, sharp edges, and other hazards.
Detect Presence
Presence-sensing devices play a vital role in detecting when a worker is too close to machinery. Upon detection, these devices can halt machine operation or prevent it from starting, significantly reducing the risk of accidents.
Emergency Stops
Emergency stop devices provide a quick way to deactivate machinery in case of an emergency. This feature is essential for ensuring that workers can respond swiftly to potential dangers.
Restrict Movements
Restraint and pullback devices limit the movement of operators’ hands, ensuring they cannot reach hazardous areas while machines are in operation. This function is critical in preventing accidental injuries.
Require Two-Hand Operation
By requiring the use of both hands to operate machinery, two-hand control and trip devices ensure that operators’ hands are kept away from danger zones, thereby minimizing the risk of injury.
Create Safe Work Procedures
Incorporating safeguarding devices into work procedures establishes safety protocols that must be followed before machinery can operate. This structured approach enhances overall workplace safety.
Educate and Train Workers
While not a physical device, training workers on the purpose and function of safeguarding devices is essential. Proper education ensures that employees understand how to use these devices effectively and maintain them appropriately.
Importance of Safeguarding Devices in the Workplace
The significance of safeguarding devices cannot be overstated. They play a crucial role in:
- Reducing Workplace Injuries: By preventing access to hazardous areas and detecting potential dangers, safeguarding devices significantly lower the risk of workplace injuries and fatalities.
- Enhancing Productivity: A safer work environment leads to fewer accidents and downtime, allowing for increased productivity and efficiency in operations.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to strict safety regulations. Implementing safeguarding devices helps organizations comply with occupational safety standards and avoid legal repercussions.
- Promoting a Safety Culture: The presence of safeguarding devices fosters a culture of safety within the workplace, encouraging employees to prioritize their well-being and that of their colleagues.
Challenges in Implementing Safeguarding Devices
Despite their importance, implementing safeguarding devices can present challenges:
- Cost: The initial investment in safeguarding devices can be significant, especially for older machinery that may require retrofitting.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the effectiveness of safeguarding devices. Neglecting maintenance can lead to malfunctions and increased risks.
- Employee Compliance: Workers must be trained to use safeguarding devices correctly. If employees do not follow safety protocols, the effectiveness of these devices is compromised.
- Tampering: Some workers may attempt to bypass or disable safeguarding devices, which can lead to dangerous situations. Organizations must address this issue through training and supervision.
Case Studies: Effectiveness of Safeguarding Devices
Several case studies highlight the effectiveness of safeguarding devices in preventing workplace injuries:
Case Study 1: Manufacturing Plant
In a manufacturing plant, the implementation of presence-sensing devices significantly reduced accidents involving operators working near automated machinery. After installing light curtains, the number of injuries decreased by 50% within the first year.
Case Study 2: Construction Site
A construction site adopted two-hand control devices for heavy machinery operations. This change led to a 40% reduction in hand injuries, as operators were required to keep their hands clear of danger zones during operation.
Conclusion
Safeguarding devices are essential tools in protecting workers from the hazards associated with machinery. By preventing access to dangerous areas, detecting presence, and requiring safe operational procedures, these devices significantly reduce the risk of workplace injuries. Organizations must prioritize the implementation and maintenance of safeguarding devices to create a safer work environment and promote a culture of safety.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main types of safeguarding devices?
A1: The main types include presence-sensing devices, pullback devices, restraint devices, safety trip controls, two-hand control devices, and two-hand trip devices.
Q2: How do safeguarding devices prevent accidents?
A2: They prevent access to hazardous areas, detect the presence of workers, and require safe operational practices, thereby reducing the likelihood of injuries.
Q3: Why is training important for safeguarding devices?
A3: Training ensures that workers understand how to use and maintain safeguarding devices effectively, which is crucial for their safety.
Q4: What challenges are associated with implementing safeguarding devices?
A4: Challenges include cost, maintenance, employee compliance, and the risk of tampering with devices.
Q5: How do safeguarding devices enhance workplace productivity?
A5: By reducing accidents and downtime, safeguarding devices contribute to a more efficient and productive work environment.
Additional Information Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Types of Devices | Presence-sensing, Pullback, Restraint, Safety Trip, Two-Hand Control |
| Functions | Prevent access, Detect presence, Emergency stops, Restrict movements |
| Importance | Reduces injuries, Enhances productivity, Compliance with regulations |
| Challenges | Cost, Maintenance, Employee compliance, Tampering |
For more detailed information on safeguarding devices, you can refer to the OSHA Machine Guarding page.