What Do Plants Need to Survive?
Plants are essential to life on Earth, providing oxygen, food, and habitat for countless organisms. Understanding what plants need to survive is crucial for gardening, agriculture, and environmental conservation. This article explores the fundamental requirements for plant survival, including water, light, air, nutrients, and temperature.
The Basics of Plant Survival
Plants are living organisms that require specific conditions to thrive. While the exact needs can vary between species, all plants share five basic requirements:
- Water
- Light
- Air
- Nutrients
- Temperature
These elements work together to support the processes that allow plants to grow and reproduce.
1. Water
Importance of WaterWater is vital for all living organisms, and plants are no exception. It serves several critical functions:
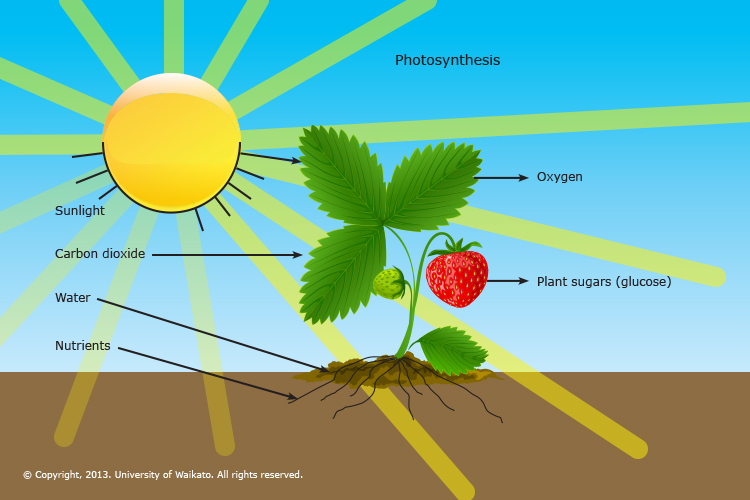
- Photosynthesis: Water is a key reactant in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
- Nutrient Transport: Water dissolves nutrients in the soil and transports them through the plant via the xylem.
- Turgor Pressure: Water helps maintain turgor pressure within plant cells, allowing them to remain rigid and upright.
How Plants Absorb WaterPlants absorb water primarily through their roots from the soil. The root hairs increase the surface area for absorption, allowing the plant to take in sufficient moisture even in dry conditions.Water Requirements Vary by SpeciesDifferent plants have varying water needs. For instance:
- Succulents: These plants store water in their tissues and require minimal watering.
- Tropical Plants: These thrive in humid environments and may need more frequent watering.
2. Light
Role of Light in Plant GrowthLight is essential for photosynthesis, where plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using sunlight. The energy captured from light fuels plant growth and development.Types of LightPlants can utilize different types of light:
- Natural Sunlight: Most plants thrive under direct sunlight; however, some prefer partial shade.
- Artificial Light: In indoor settings or greenhouses, artificial lights can supplement natural light.
Light Requirements by Plant Type
- Sun-loving Plants: Such as sunflowers or tomatoes need full sun (6-8 hours of direct sunlight).
- Shade-tolerant Plants: Ferns and certain houseplants can thrive in low-light conditions.
3. Air
Air CompositionAir is composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2). Plants require CO2 for photosynthesis.Gas Exchange ProcessPlants take in CO2 through small openings called stomata located on their leaves. During photosynthesis, they release oxygen back into the atmosphere as a byproduct.
4. Nutrients
Essential Nutrients for PlantsPlants require various nutrients to grow healthily, which can be divided into macronutrients and micronutrients:
- Macronutrients:
- Nitrogen (N): Essential for leaf growth.
- Phosphorus (P): Important for root development and flowering.
- Potassium (K): Helps with overall plant health and disease resistance.
- Micronutrients:
- Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), among others, are needed in smaller amounts but are crucial for various physiological functions.
Soil QualityThe quality of soil affects nutrient availability. Healthy soil contains organic matter that improves nutrient retention and provides a habitat for beneficial microorganisms.
5. Temperature
Temperature Range for GrowthEach plant species has an optimal temperature range for growth:
- Warm-season Plants: Such as corn or beans thrive in warmer temperatures (70°F to 95°F).
- Cool-season Plants: Such as lettuce or peas prefer cooler temperatures (45°F to 75°F).
Effects of Temperature ExtremesExtreme temperatures can stress plants:
- Heat Stress: Can cause wilting or scorching.
- Cold Stress: Can lead to frost damage or stunted growth.
Table: Basic Needs of Plants
| Requirement | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Absorbed through roots; essential for photosynthesis and nutrient transport | Maintains turgor pressure; facilitates growth |
| Light | Natural sunlight or artificial light; fuels photosynthesis | Provides energy for growth |
| Air | Composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen; CO2 is critical for photosynthesis | Enables gas exchange |
| Nutrients | Essential minerals from soil; includes macronutrients and micronutrients | Supports cellular functions |
| Temperature | Optimal range varies by species; affects metabolic processes | Influences growth rate |
FAQs
What do plants need to survive?
Plants need water, light, air, nutrients, and appropriate temperature conditions to survive.
How do plants absorb water?
Plants absorb water primarily through their roots via root hairs that increase surface area for absorption.
Why is light important for plants?
Light is crucial because it fuels photosynthesis, allowing plants to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
What nutrients do plants require?
Plants require macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, as well as micronutrients like iron and zinc for healthy growth.
How does temperature affect plant growth?
Each plant species has an optimal temperature range; extreme temperatures can cause stress that negatively impacts growth.
Conclusion
Understanding what plants need to survive is essential not only for gardeners but also for anyone interested in preserving our environment. By ensuring that plants receive adequate water, light, air, nutrients, and appropriate temperatures, we can help them thrive and continue providing vital resources to our planet.For more detailed information on plant needs, you can refer to Wikipedia.