Understanding Color Theory
Color theory is a framework used to understand how colors interact, combine, and influence each other. It encompasses different models, including the additive color model and the subtractive color model.
Additive Color Model
The additive color model is based on the principle that colors are created by combining light. This model is primarily used in digital screens and lighting. The primary colors in this model are red, green, and blue (RGB). When these colors are combined in various ways, they create other colors, including white light when all three are combined at full intensity.
- Primary Colors: Red, Green, Blue
- Secondary Colors: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow (created by combining two primary colors)
- Tertiary Colors: Created by mixing primary and secondary colors.
In the additive model, black is the absence of light. Therefore, if no light is present, the result is black.
Subtractive Color Model
The subtractive color model is used in painting and printing. It operates on the principle of color absorption and reflection. The primary colors in this model are cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY). When combined, these colors absorb (subtract) light, and the result can lead to black when all three are mixed together.
- Primary Colors: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow
- Secondary Colors: Red, Green, Blue (created by combining two primary colors)
In this model, theoretically, mixing cyan, magenta, and yellow in equal parts should produce black. However, in practice, this often results in a muddy brown. To achieve a true black in printing, black ink (K) is added, leading to the CMYK color model.
Color Mixing in Art
In the realm of art, understanding how to mix colors effectively is crucial for painters and designers. Here’s how various colors combine to create black:
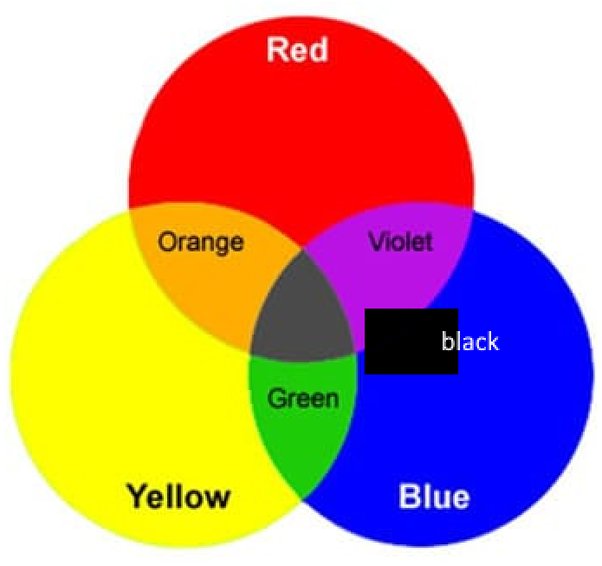
- Pigment Mixing: When mixing pigments, such as paints, the primary colors (red, blue, yellow) can be combined to create darker shades. Mixing complementary colors (colors opposite each other on the color wheel) can also yield darker tones.
- Complementary Colors: Mixing complementary colors can produce a neutral color. For example, mixing blue and orange or red and green can create a shade close to black.
Practical Applications
Understanding how to create black through color mixing has practical applications in various fields:
- Painting: Artists often mix different colors to achieve the desired shade of black or dark tones in their artwork.
- Printing: In the printing industry, the CMYK model is used to ensure accurate color reproduction, with black (K) added to ensure depth and richness in printed images.
- Digital Design: Graphic designers use RGB values to create black on screens, typically represented as (0, 0, 0).
Table: Color Models and Black Creation
| Color Model | Primary Colors | How to Create Black | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Additive (RGB) | Red, Green, Blue | No light (0, 0, 0) | Black is the absence of light. |
| Subtractive (CMY) | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow | Combine all three (C, M, Y) | Often results in brown; black (K) is added. |
| Traditional (RYB) | Red, Yellow, Blue | Mix complementary colors | E.g., Red + Green = Blackish tone. |
The Science Behind Color Mixing
The science of color mixing is rooted in physics, specifically the behavior of light and pigments. When light hits an object, some wavelengths are absorbed while others are reflected. The colors we perceive are determined by the wavelengths of light that are reflected back to our eyes.
Light Absorption and Reflection
- Light Absorption: When a color absorbs all wavelengths of light, it appears black. For example, a black object absorbs all colors of light and reflects none.
- Pigment Behavior: Pigments work by absorbing certain wavelengths of light and reflecting others. For instance, a red pigment absorbs green and blue wavelengths, reflecting red.
Color Perception
Human perception of color is influenced by various factors, including lighting conditions, surrounding colors, and individual differences in vision. The context in which colors are viewed can significantly affect how they are perceived.
Cultural Significance of Black
Black is a color with deep cultural significance across various societies. It can symbolize a range of concepts, from power and elegance to mourning and negativity. Understanding the cultural implications of black is essential for artists and designers.
Symbolism of Black
- Elegance and Sophistication: Black is often associated with luxury and sophistication, making it a popular choice in fashion and design.
- Mourning and Grief: In many cultures, black is worn during periods of mourning, symbolizing loss and remembrance.
- Authority and Power: Black can convey authority and power, often seen in formal attire and uniforms.
FAQ Section
What colors make black in pigment mixing?
In pigment mixing, black can be achieved by combining complementary colors or mixing all primary colors together. For example, mixing blue and orange or red and green can create a darker shade close to black.
How is black created in the additive color model?
In the additive color model (RGB), black is created by the absence of light. When no light is emitted, the result is black.
Why does mixing cyan, magenta, and yellow not always produce black?
Mixing cyan, magenta, and yellow often results in a muddy brown rather than a true black due to impurities in the pigments. This is why black ink (K) is added in the CMYK color model for printing.
Can I create black with just primary colors?
While you can create dark shades with primary colors (red, blue, yellow), achieving a true black may require mixing complementary colors or adding a dark pigment.
What is the significance of the color black in different cultures?
Black holds various meanings across cultures, including elegance, mourning, and authority. Its significance can vary widely depending on the context.
Where can I find more information about color theory?
For more detailed information, you can visit the Wikipedia page on color theory.
Conclusion
Understanding how to create black through color mixing is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Whether through additive or subtractive methods, the principles of color theory provide a foundation for effective color use. The cultural significance of black adds another layer of depth to its application, making it a powerful tool in visual communication.