What is the Y-Intercept?
The y-intercept of a line is the point where the line crosses the y-axis on a graph. This occurs when the value of the independent variable (usually represented by 𝑥) is zero. The y-intercept is typically denoted as 𝑏 in the slope-intercept form of a linear equation, which is expressed as:
Where:
- 𝑦 is the dependent variable.
- 𝑚 is the slope of the line.
- 𝑥 is the independent variable.
- 𝑏 is the y-intercept.
Importance of the Y-Intercept
The y-intercept provides valuable information about a linear relationship. It indicates the value of the dependent variable when the independent variable is zero. Understanding the y-intercept is crucial for:
- Graphing Linear Equations: Knowing the y-intercept allows for accurate plotting of the line.
- Analyzing Relationships: The y-intercept helps in understanding how changes in the independent variable affect the dependent variable.
- Predictive Modeling: In statistics and data analysis, the y-intercept is used in regression models to predict outcomes.
How to Find the Y-Intercept
There are several methods to find the y-intercept of a linear equation. Below are the most common approaches:
Method 1: From the Slope-Intercept Form
If the equation of the line is already in slope-intercept form (𝑦=𝑚𝑥+𝑏), the y-intercept is simply the value of 𝑏.Example:
Given the equation 𝑦=2𝑥+3, the y-intercept is 3 (the value of 𝑏).
Method 2: From Standard Form
If the equation is in standard form (𝐴𝑥+𝐵𝑦=𝐶), you can find the y-intercept by setting 𝑥=0 and solving for 𝑦.Steps:
- Substitute 𝑥=0 into the equation.
- Solve for 𝑦.
Example:
For the equation 3𝑥+4𝑦=12:
- Set 𝑥=0:
3(0)+4𝑦=12
- Solve for 𝑦:
4𝑦=12 ⟹ 𝑦=3
Thus, the y-intercept is 3.
Method 3: From a Table of Values
If you have a table of values, you can find the y-intercept by identifying the point where 𝑥=0.Example:
| 𝑥 | 𝑦 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 3 |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 7 |
From the table, when 𝑥=0, 𝑦=3, indicating that the y-intercept is 3.
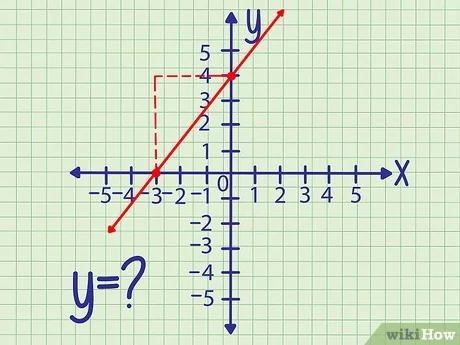
Method 4: From a Graph
If you have a graph of the linear equation, you can visually identify the y-intercept by locating the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
Examples of Finding the Y-Intercept
- Using Slope-Intercept Form:
- Equation: 𝑦=−4𝑥+2
- Y-Intercept: 𝑏=2
- Using Standard Form:
- Equation: 2𝑥+5𝑦=10
- Set 𝑥=0:
2(0)+5𝑦=10 ⟹ 5𝑦=10 ⟹ 𝑦=2
- Y-Intercept: 2
- Using a Table:
- Table:
𝑥 𝑦 -1 1 0 4 1 7 - Y-Intercept: 4 (when 𝑥=0)
- Table:
- From a Graph:
- A line crosses the y-axis at 𝑦=−1. Thus, the y-intercept is −1.
Table: Summary of Methods to Find Y-Intercept
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Slope-Intercept Form | Directly read 𝑏 from 𝑦=𝑚𝑥+𝑏 | 𝑦=2𝑥+3⇒𝑏=3 |
| Standard Form | Set 𝑥=0 and solve for 𝑦 | 3𝑥+4𝑦=12⇒𝑦=3 |
| Table of Values | Identify 𝑦 when 𝑥=0 | $$ |
| Graph | Locate the point where the line crosses the y-axis | Line crosses at 𝑦=−1 |
Applications of the Y-Intercept
Understanding the y-intercept is not only essential in mathematics but also has real-world applications:
- Economics: In supply and demand graphs, the y-intercept can represent fixed costs or base prices.
- Physics: In motion equations, the y-intercept can indicate initial position or velocity.
- Biology: In population growth models, the y-intercept may represent the initial population size.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the y-intercept?
A: The y-intercept is the point where a line crosses the y-axis, representing the value of 𝑦 when 𝑥=0.
Q: How do I find the y-intercept from an equation?
A: If the equation is in slope-intercept form, the y-intercept is the constant term 𝑏. If in standard form, set 𝑥=0 and solve for 𝑦.
Q: Can the y-intercept be negative?
A: Yes, the y-intercept can be negative, indicating that the line crosses below the origin on the y-axis.
Q: What does it mean if the y-intercept is zero?
A: If the y-intercept is zero, the line passes through the origin (0,0), meaning there is no fixed value when 𝑥=0.
Q: How is the y-intercept used in real life?
A: The y-intercept is used in various fields, such as economics, physics, and biology, to represent initial conditions or fixed values.
Q: Is the y-intercept always a single point?
A: Yes, the y-intercept is a single point on the graph where the line crosses the y-axis.
Q: Can I find the y-intercept from a graph?
A: Yes, you can visually identify the y-intercept by locating the point where the line intersects the y-axis.
Q: How do I graph a line using the y-intercept?
A: Start by plotting the y-intercept on the graph, then use the slope to determine another point on the line.
Conclusion
Finding the y-intercept is a fundamental skill in algebra and coordinate geometry. Whether using equations, tables, or graphs, understanding how to determine the y-intercept is essential for graphing linear equations and analyzing relationships between variables. Mastering this concept will enhance your mathematical skills and provide a solid foundation for more advanced topics.For more information on linear equations and graphing, you can visit the Linear Equations Wikipedia page.