How Long Does Buprenorphine Stay in Your System?
Buprenorphine is a medication commonly used in the treatment of opioid addiction and for pain management. Understanding how long buprenorphine stays in your system is crucial for patients, healthcare providers, and anyone undergoing drug testing. This comprehensive guide will explore the pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine, factors affecting its duration in the body, and practical implications for users.
What is Buprenorphine?
Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist, meaning it activates opioid receptors in the brain but to a lesser extent than full agonists like morphine or heroin. It is primarily used in medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid use disorder (OUD) and can also be prescribed for chronic pain management.
Mechanism of Action
Buprenorphine works by:
- Binding to Opioid Receptors: It attaches to the same receptors in the brain that other opioids do, but it produces less intense effects.
- Ceiling Effect: Buprenorphine has a ceiling effect, meaning that after a certain dose, taking more will not increase its effects. This property reduces the risk of overdose.
- Long Duration of Action: Buprenorphine remains active in the body longer than many other opioids, making it effective for maintaining stable medication levels in patients.
How Long Does Buprenorphine Stay in Your System?
The duration that buprenorphine remains detectable in the body varies based on several factors, including the method of administration, individual metabolism, and overall health. Here is a breakdown of how long buprenorphine can stay in different biological samples.
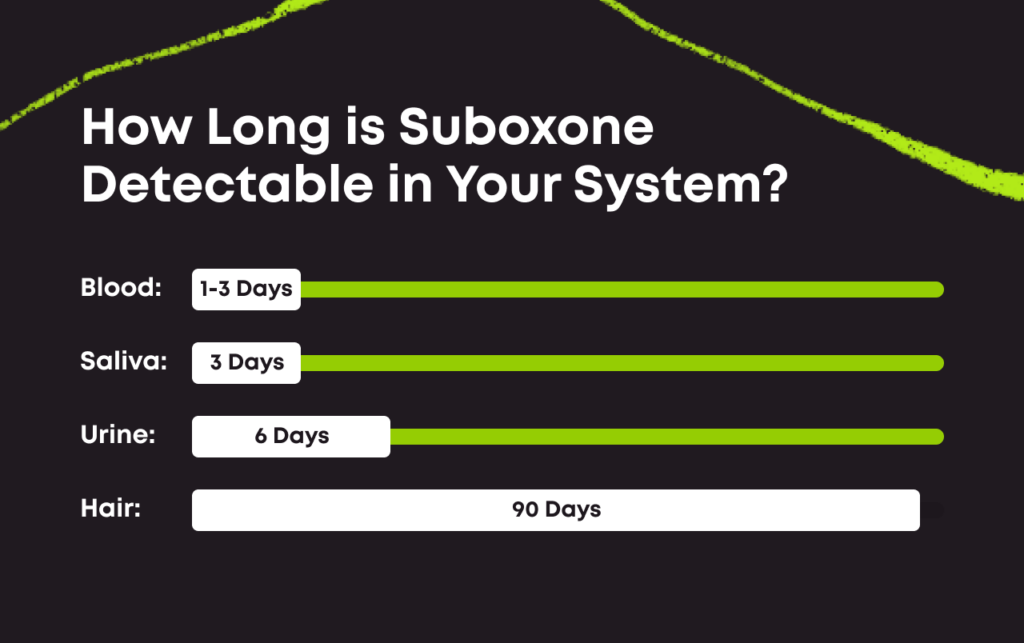
General Detection Times
- Urine: Buprenorphine can typically be detected in urine for up to 6 days after the last dose.
- Blood: It remains detectable in blood for approximately 2 days.
- Saliva: Buprenorphine can be detected in saliva for about 1 to 2 days.
- Hair: It can be detected in hair for up to 90 days.
Half-Life of Buprenorphine
The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for its concentration in the bloodstream to reduce by half. Understanding the half-life of buprenorphine is essential for predicting how long it will remain in the system.
- Sublingual Tablets: The half-life ranges from 31 to 35 hours.
- Transdermal Patch: The half-life is around 26 hours.
- Buccal Film: The half-life is about 28 hours.
- Intravenous (IV) Administration: The half-life is approximately 2.2 hours.
- Depot Injection: This long-acting formulation has a half-life of 43 to 60 days, meaning it can stay in the system for up to 10 months.
Factors Affecting Buprenorphine Duration in the Body
Several factors can influence how long buprenorphine stays in your system:
- Metabolism: Individual metabolic rates can vary significantly. People with faster metabolisms may process and eliminate the drug more quickly.
- Age: Older adults may metabolize drugs more slowly due to decreased liver function.
- Body Weight: Body composition can affect drug distribution and metabolism.
- Liver Function: Since buprenorphine is metabolized in the liver, any liver impairment can prolong its presence in the body.
- Frequency of Use: Chronic use can lead to accumulation in the body, extending the time it takes to eliminate the drug.
- Form of Administration: Different methods of administration (sublingual, transdermal, IV) have varying effects on how long the drug stays in the system.
Duration in Different Biological Samples
The duration buprenorphine stays in the system can vary depending on the type of biological sample tested. Here’s a quick look at how long buprenorphine can be detected in different samples:
| Biological Sample | Detection Time |
|---|---|
| Urine | Up to 6 days |
| Blood | Approximately 2 days |
| Saliva | 1 to 2 days |
| Hair | Up to 90 days |
Practical Implications
Understanding how long buprenorphine stays in your system is essential for various reasons:
- Medication Management: Patients should be aware of how long the drug remains active to manage their dosages effectively.
- Drug Testing: Individuals undergoing drug testing (for employment or legal reasons) should know the detection times to avoid potential issues.
- Treatment Planning: Healthcare providers can use this information to tailor treatment plans for patients based on their specific needs and circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How long does buprenorphine stay in your system after a single dose?A1: After a single sublingual or buccal dose, buprenorphine can stay in your system for about 5 to 8 days in healthy individuals and 7 to 12 days for those with liver disease.
Q2: Does buprenorphine show up on standard drug tests?A2: Buprenorphine typically does not show up on standard drug tests that screen for opioids. However, specialized tests can detect buprenorphine and its metabolites.
Q3: What factors can affect how long buprenorphine stays in my system?A3: Factors include metabolic rate, age, body weight, liver function, frequency of use, and the method of administration.
Q4: Can buprenorphine be detected in hair samples?A4: Yes, buprenorphine can be detected in hair samples for up to 90 days after the last dose.
Q5: Is it safe to stop taking buprenorphine suddenly?A5: No, it is not safe to stop taking buprenorphine suddenly without medical supervision, as this can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Always consult a healthcare provider before making changes to your medication regimen.
Conclusion
Buprenorphine is an essential medication in the treatment of opioid addiction and pain management. Understanding how long it stays in your system is crucial for effective treatment, medication management, and navigating drug testing scenarios. The duration of buprenorphine in the body can vary based on several factors, including the method of administration and individual metabolic differences.For more detailed information on buprenorphine and its pharmacokinetics, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on Buprenorphine.