Disabling Hardware Acceleration: A Comprehensive Guide
Hardware acceleration is a technology that allows software applications to offload certain processing tasks to hardware components, such as the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), to improve performance. While it can enhance the speed and efficiency of applications, it may also lead to issues such as glitches, crashes, or increased power consumption. This article provides a detailed guide on how to disable hardware acceleration across various platforms and applications, along with a FAQ section to address common queries.
Understanding Hardware Acceleration
Hardware acceleration leverages specialized hardware to perform specific tasks more efficiently than software running on the CPU alone. This process can significantly enhance performance in tasks such as video playback, gaming, and rendering graphics. However, there are instances where hardware acceleration can cause problems, including:
- Compatibility Issues: Some applications may not work well with hardware acceleration enabled, leading to rendering errors or crashes.
- Increased Power Consumption: Particularly on laptops, hardware acceleration can drain the battery faster.
- Performance Instability: Users may experience slowdowns or freezes in applications that rely heavily on hardware acceleration.
Given these potential drawbacks, users may choose to disable hardware acceleration to improve system stability or performance.
How to Disable Hardware Acceleration on Different Platforms
1. Windows Operating System
Disabling hardware acceleration in Windows can be done through various methods depending on the specific application or system settings.
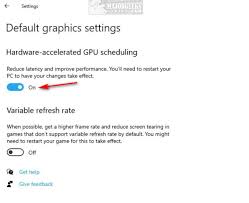
Method 1: Disable GPU Scheduling
- Right-click on the Desktop and select Display settings.
- Scroll down and click on Graphics settings.
- Toggle off the Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling option.
Method 2: Using the Registry Editor
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type
regeditand press Enter to open the Registry Editor. - Navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USER > Software > Microsoft > Graphics.
- Right-click on the right pane, select New, then choose DWORD (32-bit Value).
- Name it
HWAccelerationand set its value to0.
Method 3: Disabling Hardware Acceleration in Specific Applications
- Microsoft Edge:
- Open Edge and click on the three dots in the upper right corner.
- Select Settings.
- Click on System and performance.
- Toggle off Use hardware acceleration when available.
- Google Chrome:
- Open Chrome and click on the three dots in the upper right corner.
- Select Settings.
- Scroll down to System and toggle off Use hardware acceleration when available.
- Mozilla Firefox:
- Open Firefox and click on the three horizontal lines in the upper right corner.
- Select Settings.
- In the search bar, type performance.
- Uncheck Use recommended performance settings, then uncheck Use hardware acceleration when available.
2. macOS
On macOS, hardware acceleration is typically managed through application settings rather than system-wide settings.
- Safari: As of macOS Catalina, users cannot manually enable or disable hardware acceleration in Safari.
- Other Applications: For applications like Adobe Creative Suite or AutoCAD, check the preferences or settings menu for options related to hardware acceleration.
3. Chromebook
To disable hardware acceleration on a Chromebook:
- Open the Chrome browser.
- Click on the three-dot menu in the upper right corner.
- Select Settings.
- Click on System from the left pane.
- Toggle off Use hardware acceleration when available.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Disabling Hardware Acceleration
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Increased stability in applications | Potential decrease in performance |
| Reduced compatibility issues | Slower rendering of graphics |
| Lower power consumption on laptops | May affect video playback quality |
FAQ Section
1. What is hardware acceleration?
Hardware acceleration is a process where specific tasks are offloaded from the CPU to specialized hardware (like the GPU) to improve performance.
2. Why would I want to disable hardware acceleration?
Disabling hardware acceleration can help resolve issues such as application crashes, screen glitches, or performance instability.
3. How do I know if hardware acceleration is causing problems?
If you experience slow performance, crashes, or graphical glitches in applications, it may be worth disabling hardware acceleration to see if it resolves the issues.
4. Can I re-enable hardware acceleration after disabling it?
Yes, you can re-enable hardware acceleration by following the same steps used to disable it and toggling the settings back on.
5. Does disabling hardware acceleration affect all applications?
Disabling hardware acceleration typically affects the specific application in which it is disabled. Other applications may still utilize hardware acceleration unless changed individually.
Conclusion
Disabling hardware acceleration can be a useful troubleshooting step for users experiencing performance issues or instability in applications. By understanding how to manage hardware acceleration across different platforms and applications, users can optimize their computing experience. If you encounter persistent issues, consider consulting additional resources or seeking technical support.
References
For more detailed information on hardware acceleration, you can visit Wikipedia or explore resources on system performance and optimization through CDC.gov.This article provides a comprehensive overview of how to disable hardware acceleration, its benefits, drawbacks, and methods for various platforms and applications.